What is vitamin D and what does it do?
Vitamin D is a nutrient that works along with calcium and phosphorus to maintain healthy bones and teeth. It is also important for muscle and nerve function and a healthy immune system. Our bodies make vitamin D using energy from the sun, but the lack of sunshine in winter and use of sunscreen in summer means that we also need to get vitamin D from food and supplements.
Sources of vitamin D and how to get enough
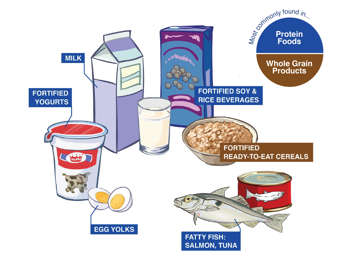
Vitamin D is mostly found in egg yolks, fatty fish and some mushrooms. Fortified foods that are also sources of vitamin D include cow's and goat's milk, margarine, plant-based milk alternatives, yogurts and cereals.
How much do we need?
Vitamin D recommendations*
| Age | Amount per day (International Units (IU)/day) |
|---|---|
| Infants (Birth – 1 year) | 400 IU |
| Children (1 – 8 years) | 600 IU |
| Children and adults (9 – 70 years) During pregnancy or lactation | 600 IU 600 IU |
| Adults (70+ years) | 800 IU |
*These recommendations are presented here simply as a guide to help you make informed food choices and are based on the expectation of minimal sun exposure.
How much vitamin D can I find a serving of food?
| Examples of food sources | Amount of vitamin D (IU) |
|---|---|
| 1 cup milk | 120 IU |
| 1 egg yolk | 45 IU |
| 2 oz cooked salmon | 400 IU |
| 1 cup fortified plant-based milk | 120 IU |
Special considerations
Vitamin D is very important for infant brain development and whole-body growth. Breastmilk does not contain enough vitamin D to meet an infant's requirements. Therefore, a vitamin D supplement is necessary for breastfed infants. If you are breastfeeding, ask your health-care provider how much vitamin D is right for your baby.
Ask your child's doctor about a supplement if your child has any digestive concerns or other conditions that cause them to absorb lower amounts of vitamin D from food.
Supplements (general recommendations)
- Infants who were born at full term that are breastfeeding or formula fed less than 1000 mL (4 cups) of infant formula need a vitamin D supplement of 400 IU each day.
- Infants who live in northern Canada need 800 IU of vitamin D per day from October to April.
- People whose skin is not regularly exposed to the sun—for example, if they work indoors, wear long clothing or head coverings, or live in northern Canada—need to choose vitamin D-rich foods or take a supplement of 200–400 IU each day.