What is calcium and what does it do?
Calcium is the main building block of our bones and teeth. If we do not get enough calcium in the diet, the body draws on the calcium reserves in the bones, making them weaker.
Sources of calcium and how to get enough
Milk and milk alternatives, dark green vegetables and fish with soft bones are sources of calcium. Dairy products, like yogurt, milk and cheese, are the best sources of calcium. For children and teens who can’t have dairy products, calcium is also found in calcium-fortified soy drinks, edamame (soybeans), tofu, broccoli, collard greens, kale, chard, Chinese cabbage and other leafy greens, almonds and sesame seeds, beans, chickpeas, oranges, figs, and prunes.
Tips
To improve the taste of milk (or calcium-fortified plant milk) for children or teens who do not like it, add a drop of strawberry or chocolate syrup. Avoid store-bought flavored milk drinks because they can have a lot of sugar.
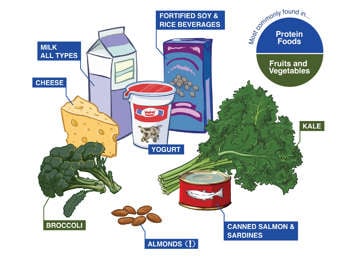
(!) Not recommended for children under four due to choking risk
How much do we need?
Calcium recommendations*
| Age | Amount per day (milligrams/day) |
|---|---|
| Birth – 6 months | 200 mg |
| 7 – 12 months | 260 mg |
| 1 – 3 years | 700 mg |
| 4 – 8 years | 1000 mg |
| 9 – 13 years | 1300 mg |
| 14+ years During pregnancy During breastfeeding |
1300 mg 1000 mg 1000 mg |
*These recommendations are presented here simply as a guide to help you make informed food choices.
How much calcium can I find in a serving of food?
| Examples of food sources | Amount of calcium (mg) |
|---|---|
| 1 cup (250 mL) milk | 300 mg |
| ¾ cup (175 mL) yogurt | 332 mg |
| 1.5 oz (50g) cheese | 245 m |
| ½ cup (125 mL) soybeans | 85 mg |
| 1 cup (250 mL) white beans | 191 mg |
| ½ cup broccoli | 33 mg |
Especially important for...
Children and teens
- Children especially need adequate calcium as they get older to support their growing bones.
Supplements and additional info
- Infants do not need a calcium supplement if they drink the recommended amount of breast milk or infant formula. However, infants need a vitamin D supplement to help them absorb the calcium in their diet.
- Infants who have started solid food can try calcium-rich foods such as soft cheese and yogurt. Once they are 12 months of age, they can have milk as a beverage. Do not exceed 2 cups/day.
- Those who are lactose intolerant can get calcium from reduced-lactose or lactose-free products such as fortified milk alternative beverages, yogurts and cheeses.
- Speak to a doctor about a calcium supplement if you or your child have osteoporosis, rheumatoid arthritis, an eating disorder or celiac disease.