What is a food label?
Food labels are found on packaged food, typically called the “Nutrition Facts Table”. These labels are there to tell you what is in your food and to help you make informed choices about food purchasing.
What can food labels tell you?
Food labels can help you:
- compare and choose foods easily to make informed decisions.
- better manage special diets where nutrition or ingredients play an important role.
- assist you in determining the nutritional value of foods.
The following guide is based on the Canadian food label.
What’s on the label?
- The Nutrition Facts table
- The ingredient list
- Optional nutrition or health claims
- Food allergen labelling
- Date labelling
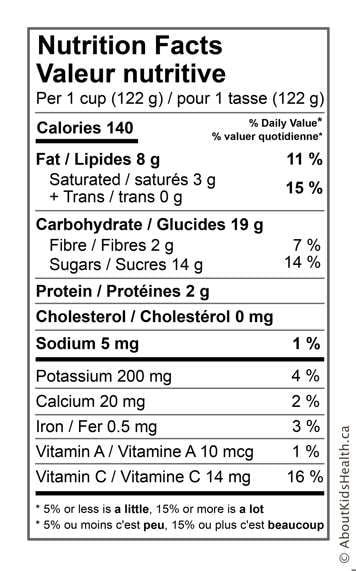
By law, most packaged foods must be labelled with a Nutrition Facts table which gives you information on:
- Serving size
- Calories
- Percent daily values (% DV)
- Information on 13 major nutrients:
An ingredient list must list all the ingredients in a food by weight, starting with the ingredient that weighs the most and ending with the ingredient that weighs the least. The ingredient list is useful to see what ingredients are in a specific product. This is especially important for people with an allergy or intolerance. Allergen information is mandatory on food labels as part of the ingredient list or on a ‘Contains’ or ‘May Contain’ list.
Some packaged food may also have nutrition claims. These claims can describe the amount of a nutrient in a food, for example: "low fat", “reduced sodium”, or make statements about the effects of a certain food on a person’s health.
How to read a label
Serving size
All information on the nutrition label is based on a specific amount of food, referred to as the serving size.
The serving size allows you to:
- understand how much of a nutrient you are eating
- compare nutrients and calories between two similar food products
- compare the serving size on the package to the amount that you eat.
If you eat the serving size shown on the Nutrition Facts table you will eat the amount of calories and nutrients that are listed on the label. It is important to make sure the serving sizes are the same if you are comparing two similar food products, such as granola bars, cereals or breads.
Here’s an example:
| Canned soup A | Canned soup B |
|---|---|
| Serving size - 125 mL | Serving size - 250 mL |
| Fibre 2 g | Fibre 2 g |
To compare the two soups correctly, the serving sizes must be the same. If you were to double the serving size of Canned soup A to 250 mL (to match Canned soup B), the amount of fibre would also double to 4 grams.
Calories
Look at the calories on the Nutrition Facts table.
Calories tell you how much energy you get from one serving of the packaged food. The amount of calories you will get will depend on how much you eat in relation to the serving size on the Nutrition Facts table. Carbohydrates, protein and fat are all made up of calories, and all of these calories are important in our diet. However, consuming too many calories, no matter where they come from could cause weight gain.
Percent daily value (% DV)
Percent daily value (% DV) is a simple way of finding out if one serving of food has a little or a lot of a nutrient. It can range from 0% to 100% and is based on the recommended daily intake of vitamins, minerals and other essential nutrients that are an important part of having a healthy diet. Depending on your age, gender and nutritional goals, you may need less or more than 100% of each of the nutrients listed. However, the % DV gives you a good idea of how much or how little of a nutrient a particular food contains. You should choose foods that contain a lower % DV of some nutrients, like fat, and a higher % DV of other nutrients, like fibre.
As a general rule, 5% DV or less is a little of a nutrient and 15% DV or more is a lot of a nutrient.
| Aim for a lower % DV | Aim for a higher % DV |
|---|---|
| Fat | Fibre |
| Saturated fat | Vitamin A |
| Trans fat | Vitamin C |
| Cholesterol | Iron |
| Sodium | Calcium |
Use % DV to compare the nutrient content of different foods. Here’s an example:
| Fruit cocktail A % DV |
Fruit cocktail B % DV |
|---|---|
| Serving size: 1/2 cup | Serving size: 1/2 cup |
| Vitamin C - 10% | Vitamin C - 20% |
Fruit cocktail B has more vitamin C because its % DV is higher. If you eat fruit cocktail B, you will be getting 20% of the recommended intake of vitamin C for the day.
Some nutrients on the food label do not have a % DV. These include:
- Protein: the amount of protein Canadians consume is generally enough, so there is no % DV.
- Cholesterol: cholesterol is not an essential nutrient because your body can make what it needs. There is no recommended intake for this type of fat, but Canadians should generally try to eat less than 300 mg of dietary cholesterol per day.
Sometimes it is not clear which food is the healthier choice. For example, one product might be low in fat but high in salt, while another one may be high in fat but low in salt. The one you choose will depend on your specific needs and requirements. You can contact a dietitian to help you determine what to focus on and the amounts you should aim for if you are unsure.
Nutrition claims
Nutrition claims are optional and must follow certain rules from Health Canada to make sure that they are consistent and not misleading. They are based on scientific evidence. There are two types of claims: nutrient content claims and health claims. Nutrient content claims describe how much of a specific nutrient is in a food. For example, 'A good source of fiber' or ‘a high source of vitamin C’. Health claims describe the effect of food on health. The following are examples of health claims:
- A healthy diet low in sodium and high in potassium may reduce the risk of high blood pressure.
- A healthy diet adequate in calcium and vitamin D may reduce the risk of osteoporosis.
- A healthy diet low in saturated and trans-fat may reduce the risk of heart disease.
- A healthy diet rich in vegetables and fruit may reduce the risk of some types of cancer.
