What are feeding tubes?
Gastrostomy tubes (G tubes) and gastrojejunostomy tubes (GJ tubes) are feeding devices. A G tube gives liquid nutrition, medication and other fluids directly into the stomach. A GJ tube gives liquid nutrition, medication and other fluids directly into the small intestine (the jejunum). Both G tubes and GJ tubes are placed through a small opening in the stomach. This opening is called a "stoma". The tunnel from the outside of the body to the stomach is called the "tract".
| The SickKids G-Tube Feeding Program has developed a one page guide to help you quickly troubleshoot any issues with your child's feeding tube: G-Tube Feeding Program Family One Pager |
What to do if your child's feeding tube is accidentally pulled out
If your child has a balloon type G tube, and it has accidentally pulled out, check if the balloon is broken. If the balloon is not broken, you may re-insert the balloon type G tube if you have learned how to do so.
If your child has a non-balloon type G tube or a GJ tube that has accidentally pulled out, it is important to insert a Foley type tube into the tract as soon as possible to prevent the stoma and tract from closing.
The Foley type catheter should be one size smaller than your child’s G or GJ tube. For example, if your child has a 16 FR tube, the Foley catheter should be 14 FR.
The sooner you insert the Foley catheter, the easier it will be to insert. You will need to carry the Foley catheter and emergency supplies with you at all times in case the tube is accidentally pulled out.
You will need the following emergency supplies:
- A Foley catheter one size smaller than your child’s tube
- A wash cloth, soap and water
- Water-based lubricating jelly
- Tape
- Sterile or distilled water
- 3 x 5mL slip-tip syringes – 1 filled with water to fill the balloon, 1 empty to check the pH and 1 filled with water to flush the tube
- pH strips
- pH colour reference guide
- An adaptor or extension set
Inserting a Foley catheter after a G tube has been accidently pulled out
The steps for inserting the Foley catheter are different depending on if your child’s G tube is new or if they have had it for a while.
Within eight weeks of getting a G tube
If your child’s G tube is accidentally pulled out within eight weeks of when it was first put in, do the following.
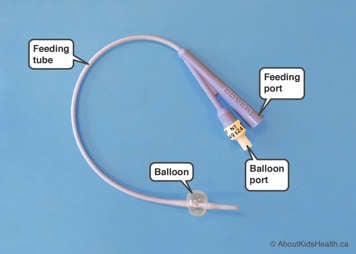
- Gather your Foley catheter and all of your emergency supplies.
- Wash your hands and the skin around your child’s feeding tube with soap and water.
- Lubricate the tip of the Foley catheter with the lubricating jelly. If you do not have lubricating jelly, you can wet the tip of the Foley catheter with water.
- Measure the Foley catheter against your index finger. If your child weighs less than 3kg (6.6 lbs), measure about 3 to 4 cm in length. This is about half the length of your index finger. If your child weighs more than 3 kg, the tube should measure 4 to 6 cm. This is the full length of your index finger.
- With your dominant hand, insert the Foley into the stoma at the length you measured. This length should be enough for the tip of the Foley catheter to reach the stomach.
- Tape the Foley catheter to your child’s abdomen.
Your child’s tract takes about eight weeks to heal after their tube is first inserted. Because the tract may not be completely healed, there is a risk that the Foley catheter may not be in the stomach. Therefore, do not use the Foley catheter to give your child feeds, fluids or medications. If your child cannot eat or drink by mouth, you may insert a nasogastric tube if you have been trained to do this. Contact your G tube specialist as soon as you insert the Foley catheter. If they are unavailable, go to the nearest emergency department as soon as possible.
Eight or more weeks after getting the tube
If your child’s G tube is pulled out eight or more weeks after it was first put in, do the following.
- Gather your Foley catheter and all of your emergency supplies.
- Wash your hands and the skin around your child’s feeding tube with soap and water.
- Lubricate the tip of the Foley catheter with the lubricating jelly. If you do not have lubricating jelly, you can wet the tip of the Foley catheter with water.
- Measure the Foley catheter against your index finger. If your child weighs less than 3kg (6.6 lbs), measure about 3 to 4 cm in length. This is about half the length of your index finger. If your child weighs more than 3 kg, the tube should measure 4 to 6 cm. This is the full length of your index finger.
- With your dominant hand, insert the Foley into the stoma at the length you measured. This length should be enough for the tip of the Foley catheter to reach the stomach.
- Tape the Foley catheter to your child’s abdomen.
- You will likely see stomach contents coming from the end of the Foley catheter. This is a good sign that the Foley catheter is in the stomach.
- If you do not see stomach contents seeping out of the Foley, you will need another way to verify the Foley is in the stomach. To do this, connect a syringe to the end of the Foley catheter and pull back. You may need to use an adaptor or extension to connect the syringe to the Foley catheter.
- Confirm that the Foley tube is in the stomach by checking the pH (acidity) of the stomach contents in the syringe. You can confirm that the Foley catheter is in the stomach by:
- checking that the stomach contents have a pH of 6.0 or less (see below for how to check the pH)
- observing that what is in the syringe looks like stomach contents
- Flush the tube with 5 mL of water to ensure the Foley is working well.
- Fill the Foley catheter balloon with the amount of water recommended on the balloon port of the tube. Use only sterile or distilled water. This will help to keep the Foley tube in place while you are feeding your child.
- Close the Foley catheter with either a catheter plug, the plunger of the syringe or an extension set.
Do not use the Foley catheter to feed or give liquids or medications until you confirm it is in the right place. Contact your G tube specialist before feeding if:
- You cannot get stomach contents back from the Foley catheter
- The pH of the stomach contents is greater than 6.0
- What you pull back from the Foley does not look like stomach contents
How to check the pH of the stomach contents
Before using the newly changed tube for feeds and medications, you will need to check that it is in the stomach by checking the pH of the contents that are pulled from the tube.
How to check the pH
You will need:
- One empty 5 mL slip tip syringe
- pH strips
- pH colour reference guide
What to do:
- Attach the 5 mL syringe to the Foley catheter. You may need to use an adaptor or extension to connect the syringe to the Foley.
- Pull back to get stomach contents. If you cannot get stomach contents, move your child side to side or sit them upright.
- Empty the stomach contents from the syringe onto a pH strip.
- Compare the colours on the pH strip to the colours on the reference guide.
If the pH is 6.0 or less, this means the Foley catheter tube is in the stomach. You can flush the tube and use the Foley catheter for feeds, fluids and medications.
If the pH is 6.0 or higher, do not use the tube for feeds, fluids or medications because the Foley catheter may not be in the stomach. Medications and recent feedings can cause the pH to be high. If the pH is 6.0 or higher, check it again in one hour. If the reading is still higher than 6.0 after one hour, do not use the Foley catheter. Contact your G tube specialist to have the position checked.
Inserting the Foley catheter after a GJ tube has been accidently pulled out
If your child’s GJ tube is accidentally pulled out, do the following.
- Gather your Foley catheter, and all of your emergency supplies.
- Wash your hands and the skin around your child’s feeding tube with soap and water.
- Lubricate the tip of the Foley catheter with the lubricating jelly. If you do not have lubricating jelly, you can wet the tip of the Foley catheter with water.
- Measure the Foley catheter against your index finger. If your child weighs less than 3kg (6.6 lbs), measure the Foley at about 3 to 4 cm in length. This is about half the length of your index finger. If your child weighs more than 3 kg, measure 4 to 6 cm in length. This is the full length of your index finger. Hold the Foley at the length your measures with your dominant hand.
- Insert the Foley into the stoma at the length your measured. This length should be enough for the tip of the Foley catheter to reach the stomach.
- Tape the Foley catheter to your child’s abdomen.
Do not use the Foley catheter to give your child feeds, fluids or medications. Call your G tube specialist. If they are unavailable, go to the nearest emergency department as soon as possible.
When a Foley catheter is used as an emergency tube, steps need to be taken to prevent movement.
To prevent a Foley catheter from moving:
- Always secure the catheter with tape to the abdomen.
- Check the water volume in the balloon at least once a week. Use sterile or distilled water to refill the balloon.
- Mark the position of the catheter where it meets your child’s stoma. You can use a permanent marker to prevent the mark from washing off with daily cleaning.
- Measure the length of the outside part of the catheter, from stoma to adaptor. This will be a reminder of how long the external length is.
To mark the catheter:
- Wash your hands with soap and water.
- Remove the tape securing the catheter to the skin.
- Pull the tube gently. When you feel resistance, stop. This is the balloon on the inner side of the tract.
- Re-tape the tube to the skin and mark the tube where it meets the stoma.
If you cannot insert the Foley catheter, contact your G tube specialist or go to the nearest emergency department.
Once the Foley catheter is in place, you will need to make arrangement to have your child's original G or GJ tube replaced.
If your child has a G tube or a GJ tube that was inserted less than 8 weeks ago, make arrangements to have their original tube replaced as soon as possible. During business hours, contact your G tube specialist. After hours, on the weekend, or during holidays, go to the nearest emergency department of the hospital that looks after your child’s tube.
If your child’s G tube had been in for eight weeks or longer, this is not an urgent situation; contact your G tube specialist on the next business day. You can use the Foley catheter to give feeds, fluid and medications for up to one month.
When to get medical help
Contact your G tube specialist or go to the nearest emergency department if:
- you cannot insert a Foley catheter after a tube has been accidently dislodged
- you cannot verify the Foley catheter is in the stomach
- your child has lots of pain after the insertion of a Foley catheter
Stop feeding and get medical help if your child has any of the following signs and symptoms after the Foley catheter is inserted:
- a hard bloated stomach
- severe pain in the stomach
- vomiting, coughing or gagging
- sudden high fever
- diarrhea
- problems with feeds and liquids getting into the lungs (aspiration)
- breathing problems