Nasopharyngeal (through the nose) and oropharyngeal (through the mouth) suctioning are done to clear secretions (mucus) from the throat if a child is unable to cough them up or swallow them. A hard-plastic tip with a handle called a Yankauer is usually used to suction secretions in the mouth.
- Gather your equipment and supplies.
- If your child uses an oximeter, make sure it is on and providing an accurate reading. Have oxygen available, if prescribed by your child’s health-care team.
-

Make sure the suction machine is at the correct setting.
-

-

Fill a clean container with sterile water or saline.
- Make sure your child is in a comfortable position (lying or sitting).
-

Attach the suction tubing to the correct size suction catheter. Keep the catheter in the packaging until just before use. Do not touch the end of the catheter that will go into your child’s nose or mouth. This illustration shows how to correctly measure the length you will need.
-

Suction a small amount of water based lubricant or sterile water/saline through the suction catheter to lubricate (wet) it and make it easier to insert.
-
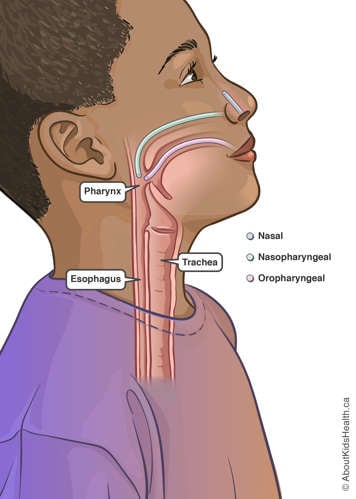
For nasopharyngeal, insert the suction catheter into your child’s nostril and to the back of the throat (nasopharynx) to the length instructed by your health-care team. Be careful not to force the catheter and rotate position as needed to guide the catheter gently. If you meet resistance, try the other nostril. Keep your thumb off the suction control port.
- For oropharyngeal, insert the suction catheter into your child’s mouth and to the back of the throat (nasopharynx) to the length instructed by your health-care team (see above illustration for reference). Keep your thumb off the suction control port.
- Apply suction by holding your thumb over the suction control port. Slowly remove the catheter while "twirling" it between your fingers to remove mucus. Limit suctioning to 5 to 10 seconds.
-

Once the catheter is out, clean it by dipping it in the sterile water or saline and suctioning. Repeat suctioning as needed, allowing at least 20 seconds between suctioning. Alternate nostrils each time you repeat the suctioning. Once you are finished, discard the catheter and replace the tip connector onto the suction tubing.
- After suctioning, assess your child’s respiratory status and oxygen needs.
-

Turn off the suction unit. Empty and clean the suction drainage bottles and containers, if needed.
-

Wash hands well. Prepare the suction equipment and supplies for the next use.
| Suction catheter size: | |
| Depth of suction catheter insertion for nasopharyngeal or oropharyngeal suctioning: | |
| Suction machine pressure setting (mmHg): |