What is hypopituitarism?
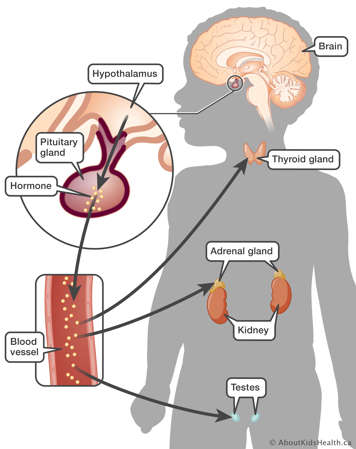
Hormones are chemicals produced in the body. They act as messengers that travel to other parts of the body where they affect how organs work. Hypopituitarism is a condition where the pituitary gland does not produce one or more pituitary hormones, or it does not produce enough hormones. "Hypo" means less than usual. The term "panhypopituitarism" means many or all of these hormones are deficient ("pan" means all).
The pituitary is a pea-sized gland located in the middle of the skull. It is part of the body’s endocrine system, which includes all of the glands that produce and regulate hormones. The pituitary gland acts as the control centre for other glands. Hormones produced in the pituitary gland impact many other parts of the body. The pituitary releases various hormones in response to chemical messages it receives from the part of the brain called the hypothalamus.
What is growth hormone (GH) deficiency?
Growth hormone is a pituitary hormone that affects the growth of bone, muscle, and other body tissues. When a child has a GH deficiency, they will have normal proportions but grow very slowly. Eventually they will be much smaller and younger-looking than other children who are the same age. These children can sometimes have a slightly chubby or "cherubic" appearance.
How is growth hormone deficiency diagnosed?
The ways to determine if a child may be GH deficient are:
- Growth rate – Review the child’s height measurements over a period of time with a comparison to their previous growth pattern, to see if their growth rate has slowed down.
- Blood sugar levels – If an infant has difficulty maintaining normal blood sugar levels it may be a sign of growth hormone deficiency.
- Blood tests:
- Diagnostic blood work may include an insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) level. IGF-1 production is stimulated by growth hormone to promote growth.
- If IGF-1 levels are low, and your child’s growth rate is low, a growth hormone stimulation test may be performed. This is a 4-hour timed test following a fasting (no eating) period. Some medication is administered intravenously (through a vein) or by mouth that stimulates the body to produce as much growth hormone as it can.
- Bone age X-ray – This is a left-hand X-ray that provides information about how slowly or rapidly the bones are maturing. Children with growth hormone deficiency often have a delayed, or younger, bone age.
How is growth hormone deficiency treated?
If your child is diagnosed as GH deficient and is growing at a slower rate, GH may be replaced with the use of synthetic growth hormone. GH is not effective if given by mouth and therefore is given subcutaneously (under the skin) by injection once a day. There are also newer long-acting GH medications given subcutaneously once weekly. GH is given until growth is complete or stopped when the adolescent reaches an acceptable adult height. For people with severe GH deficiency, later treatment during adulthood may be necessary in order to maintain overall good health. GH injections are given at home by the parents/caregivers or child.
Generally, children take GH 6 days a week. However, if it is required to keep blood sugar levels stable, GH will need to be given 7 days a week.
Side effects from taking GH are few and rare as it is a replacement therapy. For more information on growth hormone therapy, please see the document Beginning growth hormone therapy: Answers to frequently asked questions.
While receiving GH injections, your child’s growth rate is watched closely and clinic visits are scheduled every 4 to 6 months. During these visits your child’s height and weight are measured, a physical exam will take place and they will have yearly blood work and routine bone age X-rays.
Growth hormone also plays an important role in blood glucose (sugar) regulation. Infants who experience low blood sugar (or hypoglycemia) may be growth hormone deficient and may need to take daily GH injections. You may also be taught to check blood sugars with a blood glucose meter. Your health-care provider will instruct you when to check the blood sugar and give you guidelines on what to do with those results.