What is Crohn's disease?
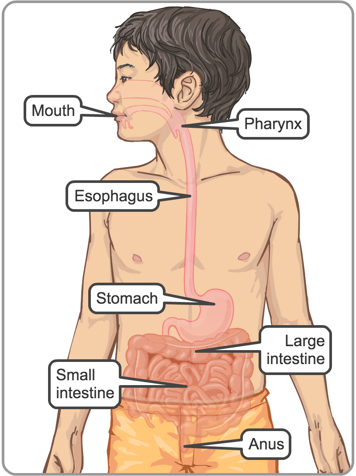
Crohn's disease (CD) is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). CD is a condition that causes inflammation in your gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Inflammation is when part of your body gets red, swollen and painful. When you have CD, all of the body parts that deal with processing what you eat from the time food goes into your mouth to the time it comes out of the other end can become inflamed.
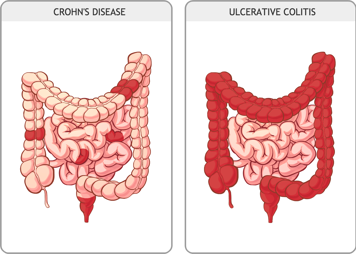
The other main type of IBD is called ulcerative colitis (UC). CD and UC are very similar, but not exactly the same. In UC, inflammation mostly happens in the colon (also called the large intestine). Your child's health-care provider will ask you questions and do certain tests to determine if you have CD or UC and will suggest treatments based on which form of IBD you have. You can get either type of IBD at any age. There are over 6,200 children under 18 years old in Canada with IBD right now, and the number of new diagnoses is rising most quickly in children under 6 years old (very early onset IBD [VEOIBD]) .
When it is too difficult to tell whether a patient has CD or UC, their IBD is classified as IBD-U. The "U" stands for unclassified; IBD-U may also be called indeterminate colitis.
Where does Crohn's disease happen?
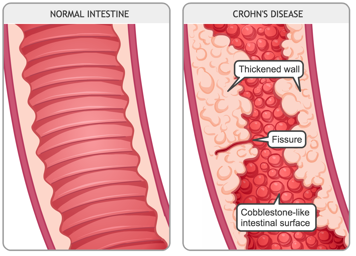
CD can occur anywhere along the GI tract, from the mouth to anus. This means that parts of your child's GI tract can be healthy while other parts are inflamed. The walls of the inflamed area thicken and develop a cobblestone-like surface. Knowing where your child has inflammation can help you, your child and their health-care provider to understand your child's symptoms and choose the right treatment.
What does Crohn's disease feel like?
What does Crohn's disease feel like? Someone with CD can have many different symptoms, like stomach pain, vomiting, loss of appetite and even fevers. They may also experience diarrhea (which can be bloody), weight loss, iron deficiency anemia, poor growth, mouth ulcers, rashes, joint pain and/or eye redness. Some people may have just a few of these symptoms, while other people may experience them all.
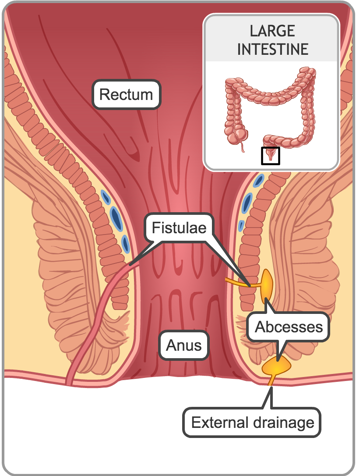
Some people may have inflammation in the anus, which could cause fissures and fistulae. Fissures are like small tears inside the anus. Fistulae are like little tunnels that connect your colon to other areas of your body that they are normally not connected to. If a fistula forms between your bowel and the skin around the anus, fluid may leak from time to time. This might make it uncomfortable to sit down. A fistula may also connect to tissues around the anus, which can become infected. This is called an abscess, and it can be painful.
CD is a chronic condition; this means that it is for life. Although there is currently no cure, there are a lot of treatment options. When you find one that helps to keep your child's CD under control, they can be in remission for a long time (that means the inflammation and ulcers have healed, and your child is "symptom-free").
What causes Crohn's Disease
Even though there have been many scientific studies, researchers do not know exactly what causes CD. They do know that it can run in families. You are more likely to get CD if you have a first degree relative, such as a brother or sister, who has it. You are even more likely to get it if that brother or sister is your identical twin. However, your life-time risk of getting CD if you have a first-degree relative with CD is only around 15%. Anyone can get CD at any age. In children and teens, it occurs slightly more often in boys than in girls.
Researchers think CD is caused by.
- Genetics: Some people may have genes in their body that increase their chances of getting CD. Studies have shown that there are over 200 genes that may be linked with IBD, but most of those genes only increase your risk a small amount. So other factors are needed to get the disease.
- Environment: Our environment includes anything our body comes in contact with. Early exposure to antibiotics, smoking cigarettes and living in a city are the most well-known types of environmental "triggers" that may contribute to IBD, but there are probably others.
- Immune system: Our immune system protects us from harmful bacteria and viruses, but in some people, it can cause inflammation in the body (such as in the GI tract).
- Gut microbiome: Lots of bacteria live in your guts, and the types of bacteria may change your risk of getting IBD.
- A combination of all these: The most common theory is that you need a combination of all the above things to get CD. For example, in people with the genes for IBD, certain environmental factors change the gut microbiome early in life, which triggers the immune system to respond later in life, causing IBD.
What kinds of treatments are there for Crohn's Disease?
There are seven types of treatments used to treat the symptoms of CD. These treatments can come in pills, liquids, intravenously (through a vein) or injections. Check with your child's health-care provider to learn more about their medications.
- 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA): 5-ASA decreases inflammation in the intestinal tract. It can be taken orally (by mouth) or rectally (in the anus/rectum). These medicines do not work very well for CD (they work for UC), but they are sometimes used for mild CD, especially if it mostly affects the colon.
- Immunomodulators: Used for long-term treatment, these drugs work by suppressing the immune system to help reduce inflammation. Immunomodulators may also help patients stay in remission. They are not intended for acute flare-ups. Immunomodulators are given orally or by injection.
- Steroids: These drugs are used for moderate-to-severe CD for a short period of time to help decrease the amount of inflammation in the body. They can be taken orally, intravenously or rectally.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics are generally effective for CD patients with an abscess, a fistula or an infection. They can be given orally or intravenously.
- Biologics: These medications act against specific chemicals (cytokines) in the body to reduce inflammation. They are often given intravenously or subcutaneously (with a needle under the skin).
- Small molecules: These medications also act against chemicals that cause inflammation but are given orally. These medications are not approved for use in children by Health Canada, but are sometimes available for some children who need them.
- Diet: Exclusive enteral nutrition (EEN), used for short-term treatment, can help patients who are malnourished because of their CD. It is also helpful to treat inflammation. It can be given orally or by a nasogastric tube. In addition, the Crohn’s Disease Exclusion Diet shows promise in treating inflammation, although we must still conduct scientific research to understand who will respond best to dietary treatments.
Sometimes when medications have failed to control the inflammation, or scar tissue has formed, surgery is done to remove the piece of bowel with inflammation. This is not a cure, but it allows for a better quality of life and for medications to work better after the surgery. There are many different types of surgeries for CD.
Recommended resources:
- SickKids IBD Centre website: https://www.sickkids.ca/en/care-services/centres/inflammatory-bowel-disease-centre/
- Crohn’s and Colitis Canada: https://crohnsandcolitis.ca/
- GI Kids (website for parents from the North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition): https://gikids.org/inflammatory-bowel-disease/
- Your Child With Inflammatory Bowel Disease (Book): https://a.co/d/91fLoJF
