What is pneumonia?
Pneumonia is an infection in the lungs. It may also be called a lower respiratory tract infection.
Community-acquired pneumonia is often caused by viruses. Pneumonia can also be caused by two types of bacteria — typical and atypical. A child can also start out by having a viral infection, which then becomes complicated by a bacterial pneumonia.
Signs and symptoms of pneumonia
Pneumonia symptoms can vary greatly in children and may be different in pneumonia caused by viruses and pneumonia caused by bacteria. Common signs and symptoms of pneumonia include:
- high and/or persistent fever
- cough
- fast breathing
- trouble breathing
- crackly noises in the lung
- loss of appetite
- vomiting due to the cough or from swallowing mucus
- feeling unwell
- abdominal (belly) pain or chest pain
What your child's health-care provider can do
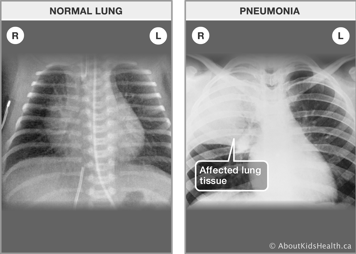
Your child’s health-care provider will listen to your child's lungs with a stethoscope and observe their breathing. If your child’s health-care provider suspects pneumonia or is concerned about their breathing, your child may have their oxygen level checked with an oxygen saturation monitor and a chest X-ray to see what their lungs look like. Not every child needs a chest X-ray, but the pattern is often different in viral and bacterial pneumonia and may help your child’s health-care provider decide if they need antibiotics. Viral pneumonia does not need antibiotic treatment. If your child’s health-care provider suspects a bacterial infection as a cause of the pneumonia, then they will prescribe antibiotics. The choice of antibiotics will depend on the most likely bacterial cause of pneumonia, how ill your child appears, the pattern on the chest X-ray and the age of your child. Your child’s health-care provider will look at many factors before deciding the best treatment.
Occasionally, children may also have a swab of the nose or throat to aid in diagnosis, but these tests are generally not required.
Taking care of your child at home
Finish all antibiotics
If your child was given antibiotics, they must finish all the pills or liquid, even if they are feeling better.
Monitor and treat the fever
To treat the fever or achy muscles, use acetaminophen or ibuprofen. You can give these medicines even if your child is also on antibiotics. They do not interact.
Keep your child fed and hydrated.
Make sure your child drinks plenty of fluids to stay hydrated. Your child may not want to eat much at first. Once the infection begins to clear and your child starts to feel better, they will want to eat more.
Avoid smoky places
Keep your child away from smoke, vaping products and other lung irritants.
Cough symptoms
Your child's cough may get worse before it gets better. As the pneumonia goes away, your child will cough to get rid of the mucus. The cough may continue for two to three weeks.
When to see a health-care provider
See your child's health-care provider if:
- your child has a fever and cough for more than three days
- you are concerned about your child's fast breathing or frequent vomiting due to cough
- your child has been diagnosed with pneumonia and their fever lasts more than three days after starting antibiotics. Some children may need other investigations, additional treatment or a change in the antibiotics that they are receiving.
Take your child to the nearest Emergency Department, or call 911 if your child:
- has difficulty breathing
- becomes very pale or blue in the lips
- vomits antibiotic doses or will not take fluid
- appears more sick
Hospital admission if needed
Most children can be cared for at home. Very sick children may need to go to the hospital. They may need oxygen, fluids given intravenously (into a vein) or other medications. They may need antibiotics given intravenously at first, and then by mouth as they get better.
Your child may show physical changes when their condition is serious or when their condition gets worse. Parents and caregivers can learn how to spot these signs in order to seek help from a health-care provider.
