What is cardiopulmonary physiotherapy treatment?
Cardiopulmonary physiotherapy treatment (CPT) is used to treat conditions that can cause mucus buildup in the lower airways of the lungs. CPT techniques can help to loosen mucus in the lungs and move it out of the airways. Clearing the airways helps to treat some types of pneumonia, which may help to improve lung function. If your child has a medical condition that causes mucus buildup in the lower lungs, CPT techniques may help to decrease the frequency of future lung infections.
If your child requires treatment, a physiotherapist can assess and determine an appropriate treatment plan for your child at home. They will also teach you how to effectively and safely add CPT into your child’s daily routine. CPT techniques your child’s physiotherapist may prescribe at home include:
- modified postural drainage (positioning)
- percussion
- expiratory vibrations
- suctioning
- mobility and play (e.g. seating strategies, tummy time, yoga ball)
CPT treatment options
Modified postural drainage
Modified postural drainage (MPD) uses gravity to help move mucus from the smaller, lower airways in the lungs up to the larger airways. The mucus is then coughed or suctioned out.
MPD is performed by placing your child in different positions, based on the location of the different segments of the lungs. This helps with drainage of the lungs. See the section below on "positioning and target area" to learn more about these positions.
MPD is usually used in combination with other CPTs such as percussion and vibrations.
Do not tip the head down for postural drainage due to the risk of reflux and subsequent aspiration.
Percussion
Percussion is used to help loosen and remove the mucus stuck to the walls of the airways.
To perform percussion, your child is placed in one of the MPD positions (see diagram _________). Then, using a cupped hand, or palm cup (see below), you will gently tap on a designated area of your child’s back or chest for approximately 3-5 minutes.
A cupped hand forms to the curve of your child’s chest and creates an air pocket that makes the percussion more comfortable for your child. As a result, the percussion should make a “hollow” sound (not a slapping sound). Percussion should be firm, but never painful, and should not create redness on the skin. A thin blanket can be placed on the chest wall for comfort.
Be careful not to percuss over your child’s spine, breastbone, stomach or ribs as this can injure your child.
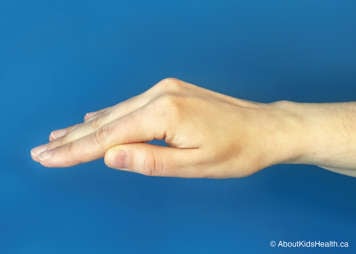

Expiratory vibrations
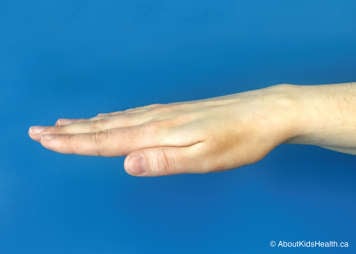
Vibrations are used to help gently shake the mucus so it can move from the smaller airways into the larger airways as a child exhales.
To perform vibrations, place your child in one of the MPD positions recommended by your child’s physiotherapist. Then, using a flat hand (see below) the caregiver places a firm hand on the chest wall over the lung segment of focus.
The caregiver tenses the muscles of the arm and shoulder to create fine oscillatory movements (vibrations) combined with compression of the child's chest wall during exhalation. The vibrations should be performed in the direction of rib movement. Exhalation should be as slow and as complete as possible.
Positioning and target area
For the following lung segments refer to the inset picture. These pictures show the correct positions for CPT. In the diagrams, shaded areas indicate hand placement where the chest should be percussed or vibrated. A physiotherapist may prescribe only specific segments, or all of them.
Note: All of these positions can be done either on a flat surface, such as a bed, or on your lap. This depends on your child’s age, comfort and needs, as well as how comfortable you feel.
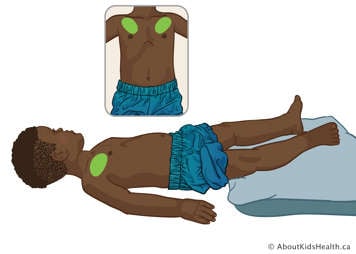
Upper lobe – anterior segments
Position your child flat on their back and treat between their collarbone and nipple. Avoid treatment over breastbone in the centre.
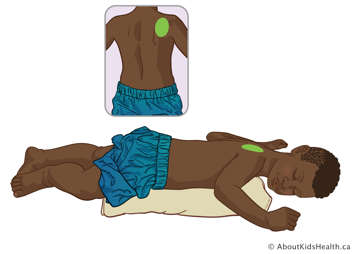
Upper lobe – right posterior segment
With your child positioned flat on their stomach, place a pillow or rolled blanket under the right side of their chest to elevate it slightly. Treat over their right shoulder blade. Avoid treating over the spine.
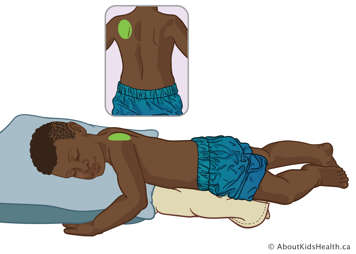
Upper lobe – left posterior segment
With your child positioned flat on their stomach place 1-2 pillows under the left side of their chest in order to elevate it 45 degrees. Treat over their left shoulder blade. Avoid treatment over the spine.
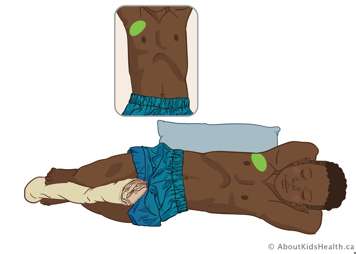
Right middle lobe
Position your child on their left side at a ¾ turn toward their back. Place a pillow or rolled blanket behind your child for them to lean back against. You can also place a blanket or pillow between their legs for added comfort. Treat close to the right armpit over nipple line .
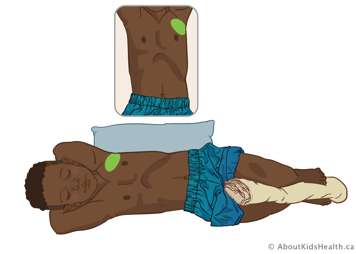
Lingula (middle of left lung)
Position your child on their right side at a ¾ turn toward their back. Place a pillow or rolled blanket behind your child for them to lean against. You can also place a blanket or pillow between their legs to stop them from rolling completely onto their back. Treat close to the left armpit over nipple line.
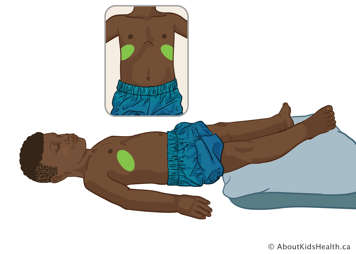
Lower lobe – anterior segments
Position your child flat on their back, with a pillow under their legs. Treat over their ribs, about two fingers above the lower edge of the ribcage. Avoid treating over the stomach and very lowest ribs.
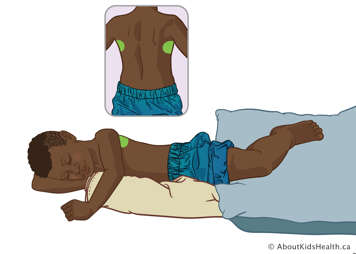
Lower lobe – lateral segments
Position your child on their right side, using a rolled blanket or pillow to support them. Treat over their left side, about two fingers above the lower edge of their ribcage. To treat the right side, position your child on their left side.
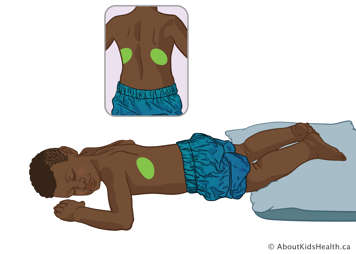
Lower lobe – posterior segments
Have your child lie flat on their stomach with a pillow under their lower legs. Treat over their ribs, about two fingers above the lower edge of their ribcage. Avoid treating over the spine.
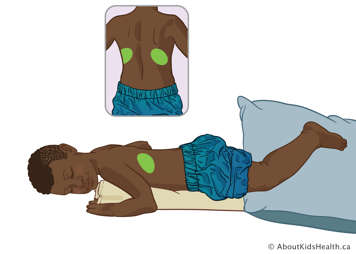
Lower lobe – posterior segments (alternative option)
Depending on their condition, some children are not able to lie flat on their stomachs. For these children, have them lie as far over onto their stomach as possible, with a blanket rolled up under their left side and a pillow between their legs to stop them from lying completely flat.
When should you stop CPT?
If your child develops increased work of breathing, stop routine CPT and seek assistance from your health-care provider. CPT could make these symptoms worse, and an assessment from a physician, nurse practitioner or trained health-care professional is needed to determine if this treatment is indicated.
Suctioning
Suctioning is a procedure that helps to clear mucus from the airway when a child cannot cough effectively.
If your child has a complex condition which could require suctioning, talk to your child’s health-care team before performing this procedure. Suctioning requires special equipment and very specific training for safety.
For more information on suctioning, please see Secretions and suctioning: General knowledge.
Cough assist
If your child has been prescribed a cough assist machine, talk to their physiotherapist to learn if this can be used in combination with your child’s regular pulmonary clearance routine.
For more information on cough assist machines, please see
Cough assist machine: How it helps to clear mucus from the lungs.
Promoting good airway clearance and ventilation
Mobility and movement are key strategies assist with pulmonary clearance and improve air entry to your child’s lungs.
If your child has a condition where lower airway secretions are retained, you can use the above treatment strategies to maintain good lung health and move the mucus out of their lungs efficiently.