Introduction
The following information provides instructions on feeding your child through their nasogastric (NG) tube by gravity.
Treatment
Feeding your child through the NG tube
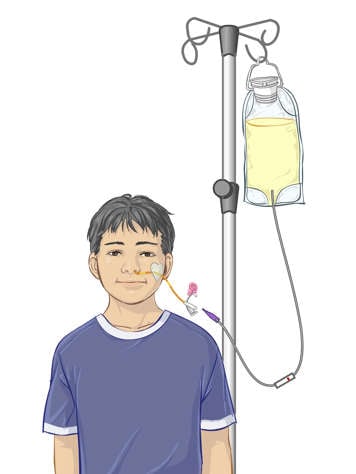
- Gather the following equipment:
- Syringe
- Liquid nutrition
- Feeding bag
- IV pole (or something to hang the feeding bag from)
- Wash your hands.


- Check the correct tube placement.
- Attach the empty syringe to the NG tube and gently flush with air to clear the tube. Then pull back on the plunger to withdraw about 2 mL of stomach contents.
- Wet the pH testing paper with the stomach contents and compare the colour with the label on the container. The pH should be 5.5 or below. You can also ask your child's health-care provider what pH to expect.
- The pH may be above 5.5 if your child is on stomach acid suppressing medications or has recently been fed. If this is the case, check if the stomach contents look like your child’s usual stomach contents. If it does not or you are unsure, do not use the tube. Remove and reinsert the NG tube, then confirm placement with pH or contact a member of your child’s health-care team.
- If the pH is above 5.5 and your child does not take stomach acid suppressing medications or has not recently been fed then the tube may not be in the stomach. Do not use the NG tube. Remove and reinsert the NG tube, then confirm placement with pH or contact a member of your child’s health-care team.
- If you have trouble pulling back stomach contents to do the pH test, try the following:
- Use a larger syringe and draw back more gently to prevent collapsing the tube.
- Push in 1 to 2 mL of air through the NG tube into the stomach and gently draw back on the syringe.
- Change your child’s position by having them lie on their left side for a few minutes to move the position of the tube in the stomach.
- If you are still unable to obtain stomach contents to test pH, consider removing the tube and reinserting it, then checking for stomach contents or contact a member of your child’s health-care team.
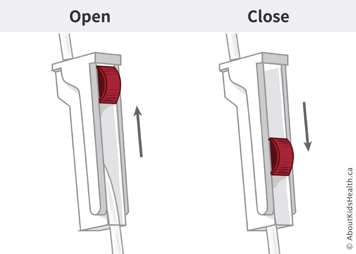
- Close the clamp on the feeding bag tubing.
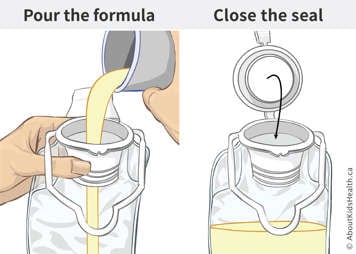
- Pour the feed into the feeding bag, close the seal tightly and hang the bag above the level of your child's stomach.
- Open the clamp to allow the feed to push all the air out of the tubing. Close the clamp once you see the fluid drip out of the end of the tubing.
- Connect the tubing to your child’s NG tube. The air in your child’s NG tube will not cause problems.
- Open the clamp slowly to get the desired flow rate. To do this, watch how fast the liquid drips in the clear drip chamber located below the feeding bag. A faster drip means the feed will go in quicker.
- Make sure the tube stays in place during the feed. Talk to your child's health-care team about ongoing or increased observation while your child is feeding using an NG tube. Children who cannot tell you their tube has moved or that they are in discomfort may need increased observation.
- When the feed is done, close the clamp and remove the feed tubing from the NG tube. Set it aside.
- If your child keeps their feeding tube in, flush the tube with 5 mL of water to clear any residue between feeds. Use 1 to 2 mL of water to flush smaller tubes.
- Cap off the NG tube.
If your child has their tube removed between feedings, wait 30 minutes after the feed, then remove the tape and gently remove the tube from their nose.
More information about the treatment
When to flush the tube
Flush the NG tube:
- At the end of every feed
- After giving medication
Cleaning your equipment
- Flush the feeding bag and tubing with warm soapy water after each feed. To rinse well, let the water flow through the tubing and into the sink. Allow the tube and bag to air dry. Replace feeding bag and tubing with a new one every seven days.
- Take apart the syringes and wash syringes with warm soapy water. Rinse well with warm, clear water and let air dry. Replace syringes with new ones every seven days.
- Syringes and feeding bags can be discarded in regular garbage bins.
Resources
For more information, please see Nasogastric (NG) tube: How to insert your child's NG tube and Nasogastric (NG) tube feeding: Common problems.
