What is the heart?
The heart is a muscle just a bit bigger than the size of your fist. It is located between the lungs, almost in the middle of the chest. It is the body's core muscle and the very first organ to form in the body after conception.
What does the heart do?
With each beat, the heart pumps blood through the body’s cardiovascular system. The cardiovascular system is made up of the heart and a system of blood vessels (the circulatory system) that help circulate blood. The blood provides oxygen and nutrients to all the organs and tissues in the body. It also delivers carbon dioxide to the lungs and the lungs then exhale to remove carbon dioxide from the body. At the same time, blood picks up waste products that are filtered out of the body by the kidneys.
What are the parts of the heart?
The right and left sides of the heart are divided by a wall called the septum. The right side pumps blood to the lungs, where the blood picks up oxygen. The left side pumps blood to the rest of the body.
The heart is made up of four hollow chambers:
- The upper two chambers are the right atrium and left atrium. These are called "collecting chambers" because they collect the blood as it returns to the heart.
- The lower two chambers are the right ventricle and left ventricle. These are called "pumping chambers" because they pump the blood out of the heart to where it needs to go.
Blood flows from chamber to chamber through the following valves, which keep blood flowing forward and prevent it from leaking backward:
- The tricuspid valve lets blood flow from the right atrium to the right ventricle.
- The pulmonary valve lets blood flow from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery.
- The mitral valve lets blood flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle.
- The aortic valve lets blood flow from the left ventricle to the aorta.
How does the heart pump blood?

After blood has travelled through the body, it comes back to the heart through the veins (vena cava) and enters the right atrium. The blood is bluish in colour because it is low in oxygen. When the heart relaxes, the blood flows through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle.
The right ventricle contracts (squeezes) to send the blood through the pulmonary valve into the arteries in the lungs (pulmonary arteries). The blood travels to the lungs, where it gets fresh oxygen and turns bright red again. It returns to the left atrium through the pulmonary veins. Then it moves through the mitral valve to the left ventricle. The left ventricle pumps the blood high in oxygen out through the aortic valve into the aorta. The aorta delivers the blood to the body and the process begins again.
What are the coronary arteries?
The heart itself is a muscle, and it needs oxygen to work. The coronary arteries branch off from the aorta. They are the vessels that bring blood high in oxygen to the heart.
The main arteries are the right coronary artery and the left coronary artery.
- The right coronary artery brings blood to the ventricles, right atrium, and sinoatrial node.
- The left coronary artery branches into the circumflex artery and the left anterior descending artery. The left coronary artery supplies the blood to the ventricles and left atrium.
This blood flow is known as coronary circulation.
What is a heartbeat?
As the heart beats, it makes a “lub-dub” sound. This is the sound made by the heart valves as they open and close. With each heartbeat, blood pushes through the aortic valve into the aorta and is delivered to the body. The heart beats about 100,000 times a day.
What is a pulse?
You can feel a pulse, the rhythmic beating of the heart, each time the ventricle contracts by touching your index and middle finger (not your thumb) to your wrist or the side of your neck. To figure out what your heart rate is, keep your fingers on your pulse and count the beats for 10 seconds, then multiply by 6.
- A newborn's heart rate is about 130 to 160 beats per minute (BPM) at rest
- A 6-month-old's heart rate is about 100 BPM
- A toddler's heart rate is about 70 to 80 BPM
- An adult's heart rate is about 60-80 BPM
How does the heart's electrical system work?
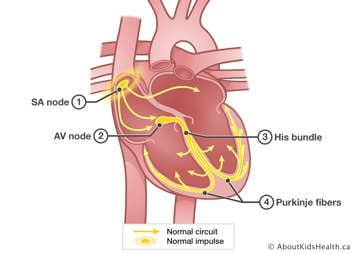
There is a small area of the right atrium called the sinoatrial (SA) node. The SA node is the body’s natural pacemaker since it controls the heartbeat.
With each heartbeat, an electrical impulse from the SA node causes the muscles of the atria to contract. This lets them pump blood to the ventricles. The electrical signal is then carried through the atrioventricular (AV) node into the ventricles, causing them to contract and pump blood out of the heart. It's similar to the motion involved when you clench and unclench your fist.
Interfering with this electrical impulse can cause problems with the heart rhythm (arrhythmias) or stop the heartbeat altogether (cardiac arrest).
In cardiology, the area of practice related to heart rhythms and the heart’s electrical system is referred to as electrophysiology.
What is blood pressure?
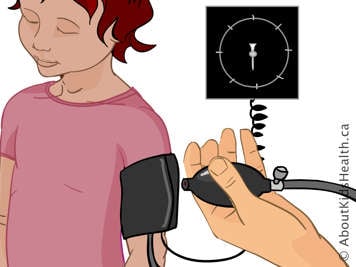
Blood pressure is a measure of the pressure of the blood against the walls of the arteries. It is expressed as a top number and bottom number. Blood pressure indicates how well the heart is pumping.
To measure your child’s blood pressure, the nurse or doctor puts a blood pressure cuff on your child’s arm. The first number measured is the systolic pressure. This is the pressure as the heart pumps blood out. The second number is the diastolic pressure. This is the pressure as the heart relaxes and refills with blood. An average adult blood pressure is 120/80. That means 120 systolic and 80 diastolic.
Children's blood pressures vary with age and activities, such as exercise and sleep. Fever can also affect a child’s blood pressure. Some typical values are:
- 75/50 for a newborn
- 96/65 for a toddler
- 100/60 for a preschooler
- 105/60 for a school-age child (6 to 8 years)
- 118/60 for a teenager
Different factors can cause blood pressure to be too high or too low. Sometimes these factors are heart-related and sometimes they are not. Your child’s health-care provider can help you understand what an appropriate blood pressure value is for your child.