Birth is a transition from a fluid environment to one where we breathe air. Breathing difficulties are common immediately after birth and during the first few hours of life. However, some babies may experience more complex breathing problems that require special care and treatment.
Transient tachypnea of the newborn
Transient tachypnea of the newborn (TTN) is a condition where breathing is rapid for a short period of time immediately after birth. Newborn babies with TTN, which is also known as "wet lung", may have the following features in addition to rapid breathing:
- retractions, also called indrawing: the muscles under the rib cage, between the ribs and in the base of the neck, move inward
- cyanosis: the gums, lips and skin appear bluish because of low oxygen levels
During pregnancy, the fetus’s lungs are filled with amniotic fluid. At birth, this fluid must be rapidly removed and replaced with air. When a baby is born vaginally, the birthing process may help to squeeze out some of the fluid, removing it from the lungs. The rest of the fluid is then absorbed by the baby's body through the lymph system and blood vessels. TTN occurs if the liquid in the lungs is not removed quickly enough. About 1 per cent of newborn babies experience TTN after birth. There is a higher risk of TTN in babies who are born by caesarean section.
TTN is diagnosed by an assessment of the newborn baby and often by X-rays. At first, it may be difficult to distinguish TTN from other causes of respiratory distress. Timing is a key factor, as TTN appears at birth or immediately after birth.
Usually, the symptoms improve on their own, but some babies need extra help with oxygen or a machine to help them breathe. The newborn baby is monitored for improvement in a special care nursery until they improve. Most newborn babies recover from TTN within three days. If the symptoms last longer, or the newborn baby needs a lot of oxygen or breathing assistance with a machine to help with ventilation, other tests may be performed to look for other diagnoses.
Respiratory distress syndrome
Newborn babies born without enough surfactant in their lungs are said to have respiratory distress syndrome or RDS. Normally, when the lungs expand with the newborn baby’s first breath, the air sacs fill with air and stay open. These air sacs are called alveoli. The reason babies can easily inflate their lungs and fill the alveoli right after birth is because the lungs are lined with a substance called surfactant. Surfactant is a kind of foamy, fatty liquid that acts like grease. Without it, the air sacs open but have difficulty staying open because they stick together. In the lungs, oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged in the alveoli. This is the essential part of breathing, and it is much more difficult to do if there is not enough surfactant at birth.
Surfactant usually appears in the fetus’s lungs at about the 24th week of pregnancy and gradually builds up to its full level by about the 35th week. Premature babies are most at risk for RDS.
RDS can be prevented in premature babies by administering steroids to the pregnant individual before delivery. After birth, the baby can receive surfactant and breathing assistance with a machine to help with ventilation. The overwhelming majority of newborn babies fully recover from RDS with no long-term lung problems. However, newborn babies with severe RDS, usually the smallest and most premature babies, are at risk for future breathing difficulties, including chronic lung disease.
Meconium aspiration
Meconium is the build-up of waste products in an unborn fetus's intestines before birth. It starts to accumulate in the intestines at around 34 weeks' gestation. Usually, the newborn baby passes the meconium in a series of bowel movements in the first few days after birth.
Sometimes, the fetus might pass some meconium into the amniotic fluid before delivery. This is most common when the baby is post-term or if the fetus experiences stress before or during birth. When meconium mixes with the amniotic fluid, there is a chance that the fetus will inhale it. This is called meconium aspiration. When this happens, the newborn baby’s air passages can become blocked, and their lungs can become inflamed. Meconium aspiration is a frequent problem in newborn babies and affects approximately 10 per cent of births. A small proportion of babies who aspirate meconium develop respiratory distress, or difficulty breathing. Some of these newborn babies require extra oxygen and breathing assistance with a machine to help with ventilation.
The treatment for meconium aspiration depends on how severe the problem is. In newborn babies who have weak or no breathing signs, a tube may be placed immediately into the windpipe to suction meconium from beneath the vocal cords. The newborn baby may need breathing assistance with a machine to help with ventilation and oxygen. Antibiotics may be started to prevent infection and pneumonia.
Meconium in the lungs tends to deactivate the fatty substance called surfactant, which is necessary for the air sacs to fill properly with air. Newborn babies with meconium aspiration may need a dose of surfactant to overcome this problem.
In mild cases of meconium aspiration, the condition subsides in two to four days. The newborn baby may have episodes of rapid breathing for a few extra days. Most newborn babies recover fully from this condition, and there usually is no lung damage. Some newborn babies with severe meconium aspiration require ventilation (breathing assistance) and a longer stay in a special care nursery.
Pneumothorax
A pneumothorax is a rupture of the air sacs, or alveoli, in the lung. When a newborn baby takes their first breath, sometimes the pressure of that breath causes some of the alveoli to tear. Air can escape through the tear to the space between the lung and the ribs called the pleural space. As more air escapes into the pleural space, it can push on the lung and prevent it from inflating. Babies who develop a pneumothorax may have rapid breathing as well as some of the signs that babies with TTN have, including retractions and cyanosis (blue colour) from low oxygen levels.
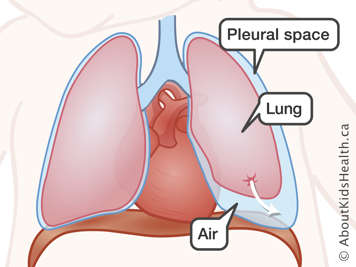
A pneumothorax is usually diagnosed or confirmed with a chest X-ray. If a newborn baby with pneumothorax has no symptoms, or only mild symptoms, no treatment may be required, and the hole will seal by itself. On the other hand, if the newborn baby is having significant difficulty breathing, then the air in the pleural cavity must be removed rapidly. This can be done using a needle and syringe. Some babies need a chest tube inserted to remove the air and allow the lung to reinflate. The tube can be removed a few days later.
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is when bacteria or viruses enter the lung and cause its airways to become infected and inflamed. The lung may produce excess fluid that can accumulate in the airways. In general, pneumonia is first suspected when the newborn baby shows unexplained signs of respiratory distress. Certain events during delivery, the condition of the pregnant individual during delivery, and indeed the type of delivery can put a newborn at risk for infection.
The first symptoms of pneumonia are:
- rapid breathing
- grunting
- retractions
- cyanosis
Other signs of pneumonia, such as a build-up of fluid in the lungs, may have other causes. This can make diagnosis difficult. X-rays may be helpful when diagnosing pneumonia, but the appearance of pneumonia on X-rays in newborns can look similar to other newborn breathing conditions. If pneumonia is suspected, babies are prescribed intravenous antibiotics for several days. These antibiotics are used to clear the infection and to prevent it from spreading to other parts of the body. Most newborn babies require extra oxygen to help them breathe while the infection clears, and some babies require breathing assistance with a machine to help with ventilation.
Congenital lung malformations
Although rare, some newborn babies are born with a congenital malformation of the lungs. These types of malformations may be suspected from prenatal ultrasound or if a newborn baby continues to experience breathing problems beyond what is expected from other more common conditions.
Generally speaking, X-rays and other imaging techniques are used to confirm a diagnosis.
There are many types of congenital lung malformations. The most common of these are:
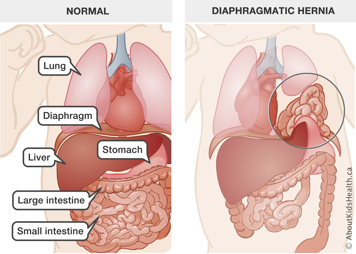
- Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: This is a malformation of the diaphragm, which separates the chest from the abdomen. Usually, with this condition, the diaphragm either is missing or has a hole in it. As a result, the organs in the abdomen—the stomach, liver, and so on—can drift into the chest cavity, leaving little room for the lungs to develop during fetal life. The lungs are smaller than usual, especially the lung on the same side as the diaphragmatic hernia. Surgery is required to repair congenital diaphragmatic hernia.
- Congenital pulmonary airway malformations (CPAM): These are abnormalities (often cysts) at the end of the small airways within the lung. Some newborns are diagnosed before birth on prenatal ultrasound and MRI and have respiratory distress at birth, while others have no immediate breathing difficulties. However, cysts in the lung usually drain poorly and cause chronic infections. All infants diagnosed with CPAM are evaluated by a surgeon and have imaging tests to confirm the diagnosis and distinguish it from other rare lung conditions. They will eventually require surgery to remove the CPAM.