What is hyperhidrosis?
Hyperhidrosis (say: hi-per-hi-DRO-sis) is the medical term for excessive (too much) sweating.
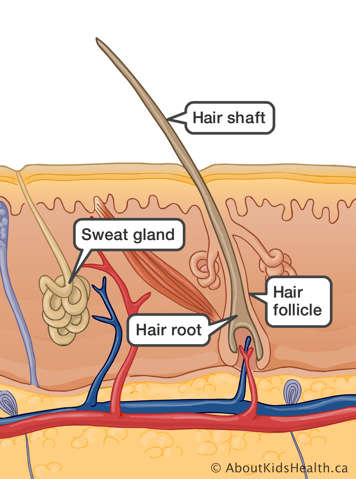
We usually sweat to keep our body temperature constant. Sweat evaporating from the skin creates a cooling effect for the body. When the body is producing much more sweat than it needs to keep cool, this is called hyperhidrosis.
Hyperhidrosis most commonly affects children, teenagers and young adults. Its onset can occur at any age and developmental stage. Increased sweating may be triggered by certain things such as anxiety, spicy foods, cola drinks, exercise, warm air temperature and fever. You may or may not be able to identify a specific trigger in your child. You should see a doctor if you think that the amount of sweat being produced is more than is needed to keep the body at a constant temperature.
Types of hyperhidrosis
There are two types of hyperhidrosis: generalized and focal.
- In generalized hyperhidrosis, excessive sweating occurs over the entire body.
- Focal hyperhidrosis occurs on a specific part of the body. This can include the underarms, soles of the feet, palms of the hands, face or other areas.
Causes of hyperhidrosis
In general, hyperhidrosis is caused by sweat glands that are too active. Generalized hyperhidrosis is most often caused by a medical condition such as:
- an infection
- a chronic disease
- a disorder that disrupts the body's natural balance of hormones
Focal hyperhidrosis is caused by a problem in the sympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system controls many automatic body functions, including sweating. This problem may be partly caused by genetics.
How hyperhidrosis is diagnosed
Physical exam
Hyperhidrosis is diagnosed by a physical exam. Sometimes, medical tests are used to rule out any condition that may be the cause of the excessive sweating.
Other tests
The doctor may do some simple additional tests to confirm the condition, such as the following:
- Starch iodine test: an iodine solution is applied to the sweaty area and then starch is sprinkled on the area. A dark blue or purple colour shows the areas of excessive sweat.
- Paper test: a special type of paper is placed on the area where excessive sweating occurs. Sweat is absorbed into the paper and then the paper is weighed. The weight of the paper shows the amount of sweat that was absorbed.
Treatments for hyperhidrosis
Topical treatments
Topical treatments are medicines that are put on the skin. Topical treatments for hyperhidrosis include antiperspirants and topical anticholinergic medicines.
Antiperspirants are used to help decrease the amount of sweating that occurs. Most people with hyperhidrosis find that normal antiperspirants do not work for them. Some antiperspirants that contain aluminum chloride may work. These can be found both over the counter and by prescription.
Topical anticholinergic medicines have also been used. These medicines block the nerve stimulation of the sweat glands, causing them to produce less sweat. These treatments may or may not work well as it is hard for the medicine to be absorbed through the skin.
Oral medicines
Sometimes, doctors recommend oral anticholinergic medicines to reduce sweating. Oral means the medicines are taken by mouth. Some examples of oral anticholinergic medicines are propantheline, glycopyrrolate and oxybutynin hydrochloride.
These medicines can cause side effects such as:
- dry mouth
- constipation (difficult bowel movements)
- increased heart rate
- urinary problems
- blurry vision
Botulinum toxin A injections (Botox)
Botulinum toxin injections are used for focal hyperhidrosis in the underarm area. Botulinum toxin blocks the signals from the nerve to the sweat gland. The injections are made into the skin with a very fine needle. Side effects can include pain at the injection site, itching and headache.
Iontophoresis
During iontophoresis (say: eye-ON-toe-for-EE-siss), each hand or foot is placed in water and an electric current is passed through the water. We do not fully understand why this treatment works, but it probably disrupts the function of the sweat glands.
This treatment may need many sessions to decrease sweating to normal levels. Side effects can include dry or peeling skin.
Surgery
Endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy (ETS) is a procedure in which the nerves that cause excessive sweating are cut. Surgery is most often a last resort for treatment of hyperhidrosis. The risks of surgery include infection, bleeding and nerve damage.
Supporting your child with hyperhidrosis
These are some of the things you can do to help your child cope:
- Educate your child about hyperhidrosis. Be honest and open with your child. Knowledge can empower and comfort them.
- Discuss the situation with your child's principal, teachers and instructors for extra-curricular activities. If they know about your child's medical condition, they will be more likely to support your child. Give your child the option of informing peers.
- Model good problem-solving and ways to cope. Demonstrate and explain to your child that it is alright to show and share their feelings. It is important that the feelings of both you and your child are addressed. If you or your child are having a hard time coping, you may want to consider speaking with a counsellor.
- Listen to your child. This condition can be extremely embarrassing for children, making it very difficult for them to talk about. Help your child establish someone they can trust and talk to.
- Encourage your child to pursue activities of interest and enjoyment, and those that may promote self-confidence and positive self-esteem. Provide your child with positive messages and praise.
- Give your child the option to interact with other children who have hyperhidrosis. This can provide support and a comfortable avenue through which your child can share experiences.
- Work with your child to set up a logbook to keep track of possible triggers and different management techniques they have experienced. Keep track of what worked and what did not work and any feelings that were raised in you and your child. This will help your child better understand and gain some feelings of control over their condition.
